From Primary Energy to New Energy: Exploring the Diverse Applications of Future Energy
When discussing new energy, it is essential first to understand the various types of energy. These terms, such as new energy, renewable energy, and green energy, might sound similar, but do they mean the same thing? Let's take a closer look!
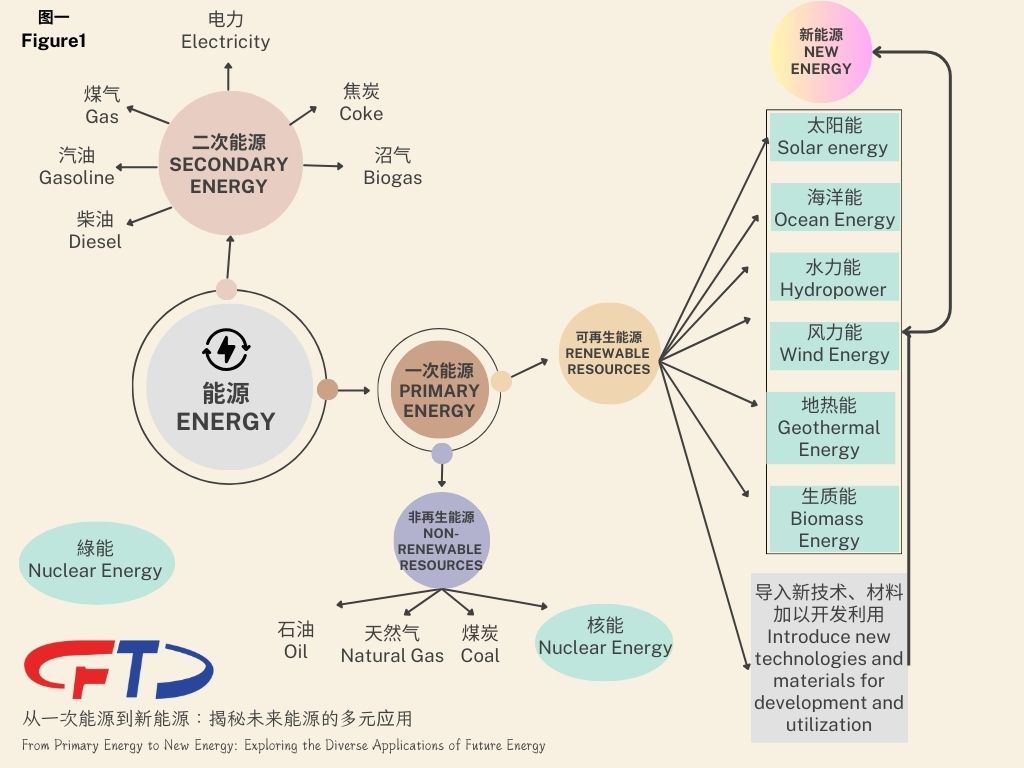
Energy can be broadly classified into primary energy, secondary energy, renewable energy, and non-renewable energy, based on how they are generated and whether they can be reused, as shown in (Figure 1).
Types of Energy
- Primary Energy:
Primary energy is energy obtained directly from nature without any transformation or conversion. This includes renewable resources such as solar, hydro, wind, geothermal, etc., and non-renewable resources like coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Secondary Energy:
Secondary energy is obtained through the processing or conversion of primary energy, including electricity, gas, gasoline, diesel, coke, and biogas.
- Renewable Energy:
Renewable energy is energy that can be replenished naturally in the environment. It is generated naturally, and the rate of replenishment is higher than the rate of consumption, meaning it won't diminish with its transformation or human utilization. This includes solar energy, ocean energy, hydropower, wind power, geothermal energy, biomass energy, and more.
- Non-Renewable Energy:
Also known as conventional energy, non-renewable energy is formed over billions of years in nature and cannot be restored in the short term. With large-scale development and utilization, the reserves are becoming increasingly scarce, eventually leading to depletion. Its use causes environmental pollution, such as oil, natural gas, coal, and nuclear fuels, which are currently heavily relied upon for power generation worldwide. It accounts for 70% of total electricity generation, including 60% from fossil fuels and 10% from nuclear energy. The remaining 30% comes from renewable energy sources.
- Green Energy:
Also known as green electricity, the definition of green energy is broader than that of renewable energy. Green energy includes renewable energy, but renewable energy does not equate to all green energy. Any energy generation with extremely low carbon emissions can be called green energy, such as solar power, wind power, and hydropower. Besides being renewable energy, they are also considered green electricity. The definition focuses on low carbon emissions rather than sustainability and continuity. Therefore, if thermal power generation can achieve extremely low carbon emissions someday, it could also be classified as green energy. In March 2021, the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC) released a significant harm assessment report on nuclear energy, stating, "The analysis found no scientific evidence that nuclear energy causes greater harm to human health or the environment compared to other electricity production technologies." Thus, nuclear power generation is declared a clean energy source because nuclear reactions do not produce air pollutants such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides, so it should be considered green energy.
- New Energy Resource:
Also known as unconventional energy or alternative energy, new energy refers to energy forms other than traditional energy that have just begun to be developed and utilized or are actively being researched. It includes energy to be promoted, or energy developed and utilized based on new technologies and materials, which are inexhaustible renewable energies like solar energy, geothermal energy, wind energy, ocean energy, biomass energy, and nuclear fusion energy (fusion reaction, nuclear fusion). However, solar energy (photovoltaic power generation) and wind power generation have been developed for many years in many countries and have a significant position, so they can no longer be considered new energy. Geothermal energy's share of national power production in China is almost negligible, so it can be considered new energy. However, it holds a large share of national power production in Kenya (51.0%), Iceland (30.0%), the Philippines (27.0%), and El Salvador (25.0%), so it can only be considered conventional energy. Therefore, the same energy method may have different names depending on the region, where it is considered new energy in some areas and conventional energy in others.
Application Fields
The new energy industry includes research, experimentation, promotion, application, and related production and business activities of new energy technologies and products. It is a high-tech field that industrializes non-traditional energy such as solar, geothermal, wind, and ocean energy. The new energy industry is an important indicator of a country or region's high-tech development level and a strategic high ground for a new round of international competition. Developed countries and regions worldwide regard developing "new energy" as an important activity to adapt to technological trends and promote industrial structure adjustment.
Conclusion
The application of new energy can reduce dependence on non-renewable (conventional) energy, achieving sustainable development goals and promoting innovation and economic development. However, it also brings some challenges and issues. The development and application of new energy technologies are revolutionary changes that require integration and coordination from multiple perspectives. Governments and enterprises need to strengthen investment and research to solve problems such as energy storage and transmission.
Fulltech Casting specializes in manufacturing precision die-castings used in new energy vehicles. Please contact us if you have any related needs.

